Ovulation Induction
Ovulation Induction is a form of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) and involves taking medication to improve ovulation. It is a first-line fertility treatment and is typically used when you ovulate irregularly or not at all.
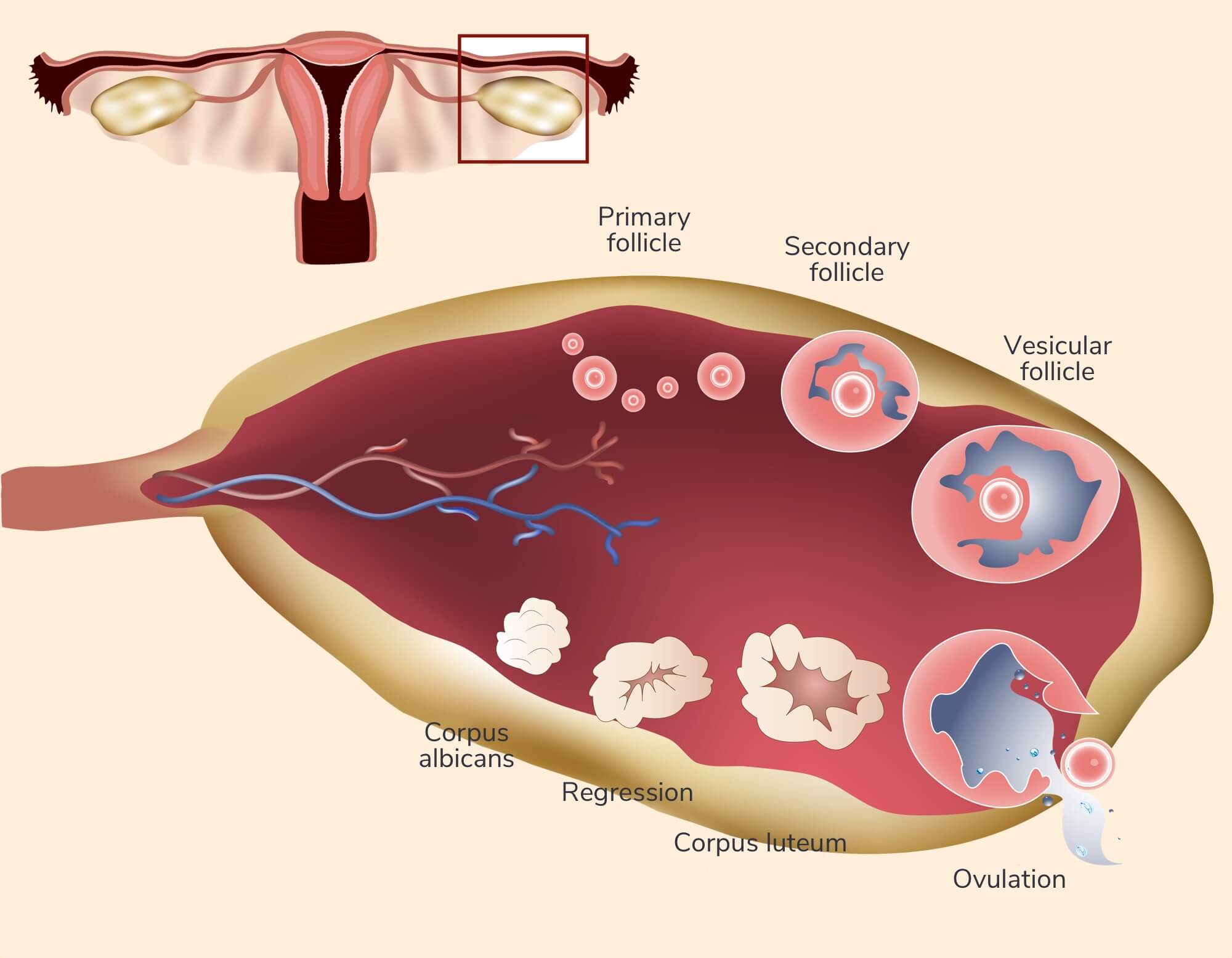
In a normal, healthy menstrual cycle, typically one egg grows, develops and matures until it is released. That release is what we call the ovulation and it typically lasts one day. Your ovulation occurs about two weeks before your next menstrual cycle starts. But not every cycle takes 28 days and the timing of the process varies for each woman, in some cases even from month to month. By using medication and monitoring your cycle, Ovulation Induction may help you fall pregnant.
What is Ovulation Induction?
With Ovulation Induction, as a woman you take hormones at the beginning of your menstrual cycle. They can be taken either in the form of a tablet or as daily injections. During that time you will be monitored with blood tests and ultrasounds. Your fertility specialist will establish when your ovulation is due and they will recommend a specific timeframe to have intercourse with your partner.
Ovulation Induction may be a first-line treatment for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Often they have irregular periods or they don’t menstruate and ovulate at all.
Step 1: Initial consultations
During the initial consultations, your fertility specialist will initiate and prescribe a series of tests, formulate a diagnosis and set up your fertility treatment plan.Step 2: Start medication
Your treatment starts at the beginning of your menstrual cycle. Your ovaries will be stimulated with medication to encourage the growth of follicles that contain the eggs.Step 3: Monitoring
You may be monitored with ultrasounds and blood tests to control the amount of follicles and their size. With simple oral treatment ultrasound testing may not be undertaken.Step 4: Trigger injection
Sometimes patients will be administered a trigger injection (an injection of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin or hCG) to assist with the final maturation of the egg and loosening of the egg from the follicle wall. Whether you need a trigger injection and timing of the trigger injection depends on your individual situation (i.e. size and the amount of follicles).Step 5: Timed sexual intercourse or IUI
Depending on your situation, you will start timed sexual intercourse or you may be asked to attend your fertility clinic for a procedure: an Intrauterine Insemination.Step 6: Pregnancy test
Your fertility clinic will inform you to attend a collection or pathology centre for a blood test at a specific time, typically 16 days after your ovulation.Ovulation Induction treatment may be recommended for:
- Women with unexplained infertility.
- Women who are not ovulating or ovulating irregularly.
- Women with long, irregular or infrequent cycles.
- Women with PCOS (Poly-Cystic Ovarian Syndrome).
It is less likely to be recommended if:
- You have tubal blockage or tubal damage.
- You have severe endometriosis.
- There is any male-factor infertility.
- The woman undergoing the treatment is over 38 years of age.
Ovulation Induction risks
In some women, fertility medication causes a risk of OHSS or Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, excessive weight gain, and dehydration. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to contact your fertility clinic immediately. In mild cases, OHSS may improve on its own, while severe cases may require hospitalisation and additional treatment.

